We are using two long-term forest diversity experiments in SW Finland, one of which is manipulating tree species diversity and another one manipulating within-species genetic diversity. Taken together, these experiments provide a unique opportunity to compare effects of trees species and intraspecific genetic diversity on forest ecosystem functioning and services.
The tree species diversity experiment
The Satakunta tree species diversity experiment was established in spring 1999 on three clear-cut areas (about 1.5-2 ha each) located 20-30 km from each other in the Satakunta area, south-western Finland (61°N, 22°E).
Tree species diversity was manipulated by planting monocultures and mixtures of the following 5 tree species :
Silver birch (Betula pendula) – deciduous broadleaf, economically important for Finland
Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) – evergreen conifer, economically important for Finland
Black alder (Alnus glutinosa) – deciduous broadleaf, nitrogen-fixing species
Norway spruce (Picea abies) – evergreen conifer, economically important for Finland
Siberian larch (Larix sibirica) – deciduous conifer, exotic species commonly grown in Finland
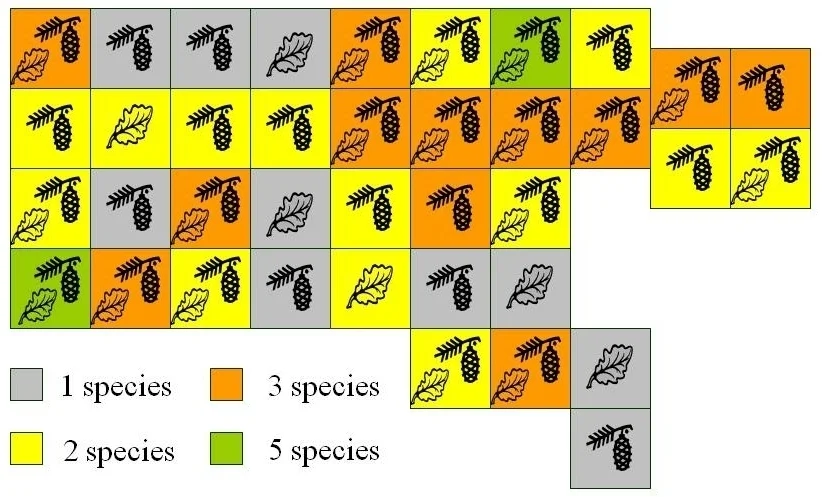
Each area contains 38 plots randomly allocated to 19 treatments (monocultures and various mixtures of 5 tree species, Table 1). There are 2 replicates of each treatment per area (6 replicates altogether). Species mixtures are composed in such a way that they represent a gradient from completely coniferous forest (pine, spruce and larch) through mixed conifer/deciduous stands to deciduous ones (birch and alder).
Table 1 : Species composition treatments for the species diversity experiment
Plots are 20 m x 20 m and contain 13 rows with 13 seedlings in each row (i.e., 169 seedlings per plot) planted at 1.5 m intervals. In mixed stands, different tree species are present in equal proportions (50 : 50, 33 : 33 : 33 or 20 : 20 : 20 : 20 : 20), but tree positions within a plot are randomized to mimic natural stands. Tree material used in this experiment originated from a local tree nursery, is genetically diverse and of local southern Finnish provenances.
One replicate of each treatment within area was thinned in 2013, providing the opportunity to compare tree species diversity effects at two different densities.
Layout of the plots on one of the Satakunta areas.
Within plot design of a 2-species plot in Satakunta
In 2014, canopy was almost closed.
Birch-Alder plot in 2014
THE BIRCH CLONE DIVERSITY EXPERIMENT
The Satakunta birch clone diversity experiment has been established in 2000. It consists of a single 2 ha area located within 20 km from the Satakunta tree species diversity experiment, containing 48 20 x 20 m plots planted with 8 different genotypes of silver birch. The eight silver birch genotypes used in the experiment are of southern Finnish origin (61-63°N) and have been obtained by micropropagation of vegetative buds of mature trees. The eight clones selected for the experiment are known to differ in their growth and leaf characteristics as well as in resistance to herbivores and pathogens.
Plots are randomly assigned to the following genotypic diversity treatments: single-genotype plots, two-genotype mixtures (5 different combinations), four-genotype mixtures (5 different combinations), and an eight-genotype mixture. Each particular genotype combination is replicated 2-6 times within the experimental area, allowing separation of effects of genotype diversity and genotype composition. In mixed stands, different birch clones are planted in equal proportions and their positions within plots are randomized. We have originally planted 100 trees per plot (10 rows, 10 trees in each at 2 m intervals). The experiment was thinned in 2013 to reduce tree density by half while keeping proportions of different clones equal.
Birch clone plots in 2015